
Clinical Excellence
Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur is committed to upholding the highest standards of clinical integrity in all aspects of patient care.
Here, we highlight our dedication to clinical performance, which encompasses our commitment to delivering quality care, patient safety, and positive outcomes. We understand that achieving clinical excellence requires a multi-faceted approach, which is why we continually invest in the latest technologies, invite the most skilled medical professionals to join us, and improve our processes and procedures.
Our goal is to provide our patients with the best possible outcomes and experiences while ensuring that we maintain our commitment to clinical integrity.
- Patient Safety and Quality Data
Our Commitment to Patient Safety and Quality
Patient safety is simply defined by the World Health Organization as “the prevention of errors and adverse effects to patients associated with health care”.
At Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur, patient safety is paramount. Every day we work together to deliver effective and efficient care while protecting our patients from harm.
We have created a culture where emphasis is given to patient safety, ultimately increasing awareness and trust as healthcare providers via communication and leadership. Our main components of patient care delivery listed below are continuously reviewed, analyzed, and improved.
- Timely and effective access to care
- Safe patient care following International Patient Safety Goals (IPSG)
- Adherence to evidence-based practices which results in better patient outcomes and lower costs of care for consumers
- Integrated clinical and operational data
International Patient Safety Goals (IPSG)
- Patient Identification
- Effective Communication
- Safety of High Alert Medications
- Safe Surgery
- Reducing the risk of healthcare associated infections
- Reducing the risk of patient harm resulting from falls
Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur prides on our excellent patient safety measures and outcomes as a result of our strict infection control protocols.
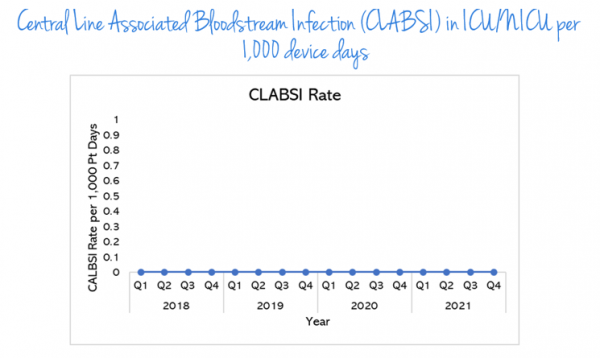
Central line Associated Bloodstream infections (CLABSI) in ICU/nICU per 1,000 device days
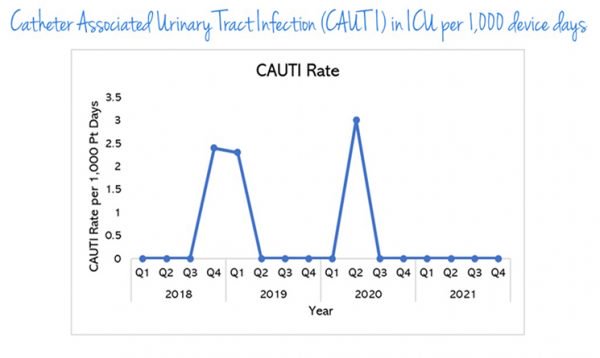
Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) in ICU per 1,000 device days
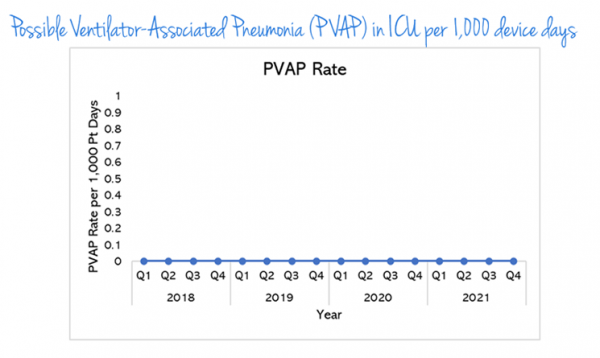
Possible Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (PVAP) in ICU per 1,000 device days
Possible Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (PVAP) in ICU per 1,000 device days
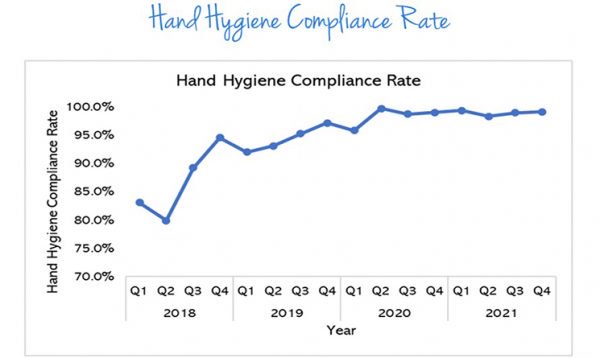
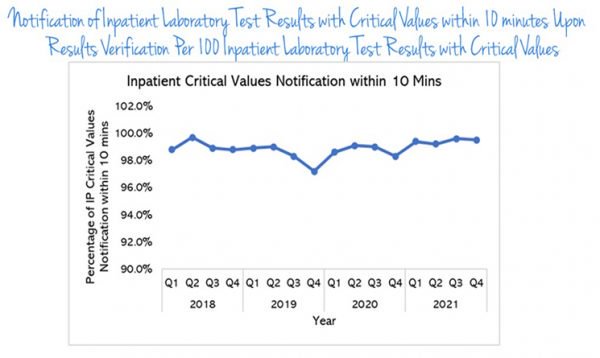
Hand Hygiene Compliance Rate
- Value Driven Outcomes (VDO)
Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur’s value-driven outcomes, or Value Driven Outcomes (VDO), seek to improve quality and end-results for our patients while rationalizing the costs required to provide the desired quality care and outcomes for patients.
How does Value Driven Outcomes (VDO) work?
Value Driven Outcomes (VDO) is a patient-centered tool. It enables the application of quality measures which are tailored to suit each medical condition. Throughout the patient’s care journey, processes are then put in place to track such quality outcomes eg: timeliness of administrating antibiotics, speed of recovery of patients following a surgical procedure, accuracy, and effectiveness of scopes, etc.
What it means for Our Patients?
One of the key parameters of quality is patients’ perspective of the care they have received in terms of patient satisfaction and the speed of their recovery or better function after their hospital stays. Value Driven Outcomes (VDO) also aspires to provide high-quality, cost-efficient care that is safe, appropriate, and effective. In addition, patients can be reassured that they will receive evidence-based care, with proven treatments and techniques.
VDO also results in patients being cared for by better organized and coordinated teams of healthcare personnel, as healthcare providers are better equipped with quality data which enables them to make more accurate assessments and decisions regarding patient care.
What has Value Driven Outcomes (VDO) achieved for us?
We are encouraged by the results we have seen. We are convinced that by using sophisticated data-harvesting technologies like Value Driven Outcomes (VDO) in our healthcare institution, we will be able to alter the way they provide care to patients. We are continuing to work on implementing more Value Driven Outcomes (VDO) initiatives across all the institutions within Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur.
What It Takes for Value Driven Outcomes (VDO) to Work?
Value Driven Outcomes (VDO) in Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur
Upcoming Value Driven Outcomes (VDO)
- Breast Cancer
- Antimicrobial Stewardship (AMS) Data
In Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur’s AMS program, we closely track antimicrobial use, monitor processes and measure outcome indicators. The effect of stewardship initiatives on antimicrobial use and resistance patterns is then analysed by our AMS team. This information is then used to provide feedback to our consultants.
General Role of Antimicrobial Stewardship Team
- Promotion of optimal selection of antibiotic regimen
- Prevention of antibiotic resistance
- Ensure improved patient treatment outcomes
- Improvement of antibiotic susceptibilities to targeted antibiotics
- Driving down of patient and hospital costs
Antibiotic Stewardship in Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur
2-set Blood Culture2 sets/samples – accuracy, scoring to deep dive susceptibility quantitative A blood culture is a laboratory test in which blood, taken from the patient, is inoculated into bottles containing culture media to determine whether infection-causing microorganisms (bacteria or fungi) are present in the patient’s bloodstream.
Blood cultures are intended to:
- Confirm the presence of microorganisms in the bloodstream
- Identify the microbial aetiology of the bloodstream infection
- Help determine the source of infection (e.g., endocarditis)
- Provide an organism for susceptibility testing and optimization of antimicrobial therapy
AntibiogramsWhat is an antibiogram?
An antibiogram is an overall profile of antimicrobial susceptibility testing results of a specific microorganism to a battery of antimicrobial drugs.What are antibiograms used for in Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur?
Antibiograms help guide our consultants and pharmacists in selecting the best empirical antimicrobial treatment in the event of pending microbiology culture and susceptibility results.
They are also useful tools for detecting and monitoring trends in antimicrobial resistance in our hospital. When antimicrobial susceptibility testing data is summarized cumulatively, we can identify and investigate trends in resistance.BCID2 PanelBlood Culture Identification 2 (BCID2) Panel enables rapid and accurate automated detection of pathogens and antibiotic resistance genes associated with bloodstream infections. Positive blood culture sent for PCR to obtain exact organism + resistance gene – reduce delay in starting right abx, reduce mortality, prevent CRRT, cost, start tx early, reduce ICU admission, less chance of reducing HAI
Gram+ Bacteria Gram- Bacteria Enterococcus faecalis Acinetobacter calcoaceticus- baumannii Enterococcus faecium Bacteroides fragilis Listeria monocytogenes Enterobacterales Staphylococcus Enterobacter cloacae complex Staphylococcus aureus Escherichia coli Staphylococcus epidermidis Klebsiella aerogenes Staphylococcus lugdunensis Klebsiella oxytoca Staphylococcus lugdunensis Klebsiella oxytoca Streptococcus Klebsiella pneumoniae group Streptococcus agalactiae Proteus Streptococcus pyogenes Salmonella Streptococcus pneumoniae Serratia marcescens Haemophilus influenzae Neisseria meningitidis Pseudomonas aeruginosa tenotrophomonas maltophilia Yeast Antibiotic Resistance Candida albicans Carbapenemases Candida auris IMP Candida glabrata KPC Candida krusei OXA-48-like Candida parapsilosis NDM Candida tropicalis VIM Cryptococcus neoformans/gattii Colistin Resistance mcr-1 ESBL CTX-M Methicillin Resistance mecA/C mecA/C and MREJ (MRSA) Vancomycin Resistance vanA/B Pneumonia Plus Panel (ICU/CCU/HDU)Enables rapid and accurate automated testing for bacteria and viruses that cause pneumonia and other lower respiratory tract infections (LRTI), as well as for genetic markers of antibiotic resistance. Especially for ill patients in ICU/CCU/HDU, the panel testing uses samples of trachea aspirate or bronchoalveolar lavage for investigations and the type of bacteria can be known within 1 hour. This is a very specific and targeted and has produced great outcomes for our patients in Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur.
Bacteria (semi quantitative) Antibiotic Resistance Genes Acinetobacter calcoaceticus-baumannii complex ESBL Enterobacter cloacae Escherichia coli Carbapenemases Haemophilus influenzae KPC Klebsiella aerogenes NDM Klebsiella oxytoca Oxa48-like Klebsiella pneumoniae group VIM Moraxella catarrhalis IMP Proteus spp Pseudomonas aeruginosa Methicilin Resistance Serratia marcescens mecA/mecC and MREJ Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus agalactiae Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcus pyogenes Bacteria (Qualitative) Viruses Legionella pneumophila Influenza A Mycoplasma pneumoniae Chlamydia pneumoniae Influenza B Adenovirus Coronavirus Parainfluenza virus Respiratory Syncytial virus Human Rhinovirus/Enterovirus Human Metapneumovirus Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV)* Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur Antimicrobial Stewardship Activities
- Formulation of Local Guidelines & Clinical Pathways
Local antibiotics guidelines & clinical pathways are formulated based on the national antibiotic guideline, evidence in the literature and local microbiology and resistance patterns.
- Surveillance and Feedback
- Collection and analysis of local antimicrobial consumption and expenditure:
- Data collection and analysis of antimicrobial use and expenditure is undertaken monthly for critical and non-critical cases
- The results of antimicrobial use and expenditure is fed back to prescribing clinician and results and outcome discussed by Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur HIACC team in relevant meeting.
- Consulting AMS team for suggestions to reduce resistance
- Reduction in patient and hospital costs
- Early discharge for patients
- On-ground indicators for reporting antibiotic consumption:
- Daily Defined Dose (DDD) per 100 patient admission
- Provision of data to regional /national surveillance programs
- The data is reported and presented at local and state level. It also is submitted to Pharmaceutical Services Division for National Surveillance on Antibiotic Utilisation?
- Antimicrobial Order Tools
- Antimicrobial Order Tools
- Antimicrobial Selection and Dose Optimization
- extended or continuous infusion of beta-lactams
- aminoglycosides and vancomycin – therapeutic drug monitoring
- appropriate dosing of antimicrobials (e.g.; vancomycin, polymyxins, cefepime)
- weight‐based dosing of certain antimicrobials
- dose adjustments for patients with renal dysfunction including AKI, HD, CRRT
- preparing loading dose of antibiotics
- prolonged infusion of antibiotics
- individualized optimized dosing based on patient‘ condition (renal function test/liver function test/etc.)
- Intravenous (IV) to Oral (PO) Antibiotics Conversion
- Education Programmes
Outcome:
By filling in the antimicrobial order tools, the prescribers also provide themselves the data for drug utilisation surveillance. Antimicrobial order tools can be an effective measure to decrease antimicrobial consumption by implementing automatic stop orders and/or requiring clinicians to justify antimicrobial use
De-escalation of antibiotics done
Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur Strategies for dose optimization include:
Selection of antimicrobials - AMS will advise consultants based on organisms.
Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PKPD) optimization done by:
HIACC Meeting –
Frequency: 4 times a year
Outcome: Updates to consultants every meeting on DDD dataPantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur HIACC Team
- Chairperson: Head of HIACC (Appointed by MDAC Chairman in Consultation with PIC)
- Membership: Four (4) consultants appointed by the HIACC Chairman, Microbiologist, Director of Nursing, Infection Control NUrse, Head of Laboratory Services, Operating Theatre Manager, ICU Nurse Manager, Pharmacy Manager, Environment Safety & Health Officer, Housekeeping Manager, Facilities Manager. Hospital‘s CEO, PIC and Head of MAQ, PPL MOD (or their representatives) as ex-officio members.
- By Invitation:
- Medical Affairs and Risk Department Representative
- Other HODs / Managers / staff as required
- Secretariat: Senior Infection Control Nurse
- Breast Imaging Score (BI-RADS)
What does BIRADS on your mammography/ ultrasound report mean?
BI-RADS (Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System) is a risk assessment and quality assurance tool developed by American College of Radiology that provides a widely accepted lexicon and reporting schema for imaging of the breast.
Classification
Breast imaging studies are assigned one of seven assessment categories:
- BI-RADS 0: incomplete
- need additional imaging evaluation (additional mammographic views or ultrasound) and/or
- for mammography, obtaining previous images not available at the time of reading
- BI-RADS 1: negative
- symmetrical and no masses, architectural distortion, or suspicious calcifications
- BI-RADS 2: benign
- 0% probability of malignancy
- BI-RADS 3: probably benign
- <2% probability of malignancy
- short interval follow-up suggested
- BI-RADS 4: suspicious for malignancy
- 2–94% probability of malignancy
- for mammography and ultrasound, these can be further divided:
- BI-RADS 4A: low suspicion for malignancy (2–9%)
- BI-RADS 4B: moderate suspicion for malignancy (12–49%)
- BI-RADS 4C: high suspicion for malignancy (50–94%)
- biopsy should be considered
- BI-RADS 5: highly suggestive for malignancy
- >95% probability of malignancy
- appropriate action should be taken
- BI-RADS 6: known biopsy-proven malignancy
When used appropriately, the BI-RADS assessment categories accurately reflect their positive predictive value for cancer, which are on average as follows for mammographically identified lesions that underwent biopsy:
BI-RADS 2: 0%
BI-RADS 3: 2%
BI-RADS 4: 30%
BI-RADS 5: 97%
Case Study: Accuracy of radiologists’ report vs biopsy report
Indroduction: Early diagnosis is crucial for the treatment and prognosis of breast cancer. Numerous studies have reported on the false-negative findings on ultrasound and mammogram and the fears of missing a malignant lesion in the early stage have led to aggressive biopsy. In year 2003, the American College of Radiology standardised diagnostic characterisation of ultrasound-detected breast lesions in the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) atlas.
Objectives: The aims of this study are to evaluate the accuracy of ultrasound-guided biopsy for the diagnosis of breast cancer in a single centre and to analyse the concordance between radiological BI-RADS scoring and histology findings.
Methodology: This is a retrospective observational study. All patients underwent ultrasound-guided core-needle breast biopsy from the year 2017–2019 in the centre were included in the analysis. Concordance were defined as agreement between radiology and pathology results. BI-RADS 4 and 5 were defined as probably malignant and BI-RADS 3 were defined as probably benign.
Results: A total of 688 patients were included into this study. The mean age was 45.0 (±12.4) years. Four hundred sixty–four (67.4%) lesions were found to be benign and 224 (32.6%) lesions were found to be malignant. The most common lesion detected was invasive ductal carcinoma (27.8%) followed by fibroadenoma (25.1%). The positive predictive value for BI–RADS 5 is 94.9% while the negative predictive value for BI–RADS 3 is 95.8%.
Conclusion: Regular audit in breast imaging based on international recommendations provide quality assurance data to improve the quality of patient care.
How has BIRAD scoring helped Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur patients?
- Accuracy in diagnosis
- Assurance and peace of mind
- No unnecessary biopsy done on patients
- Cost reduction




.webp?sfvrsn=20763f7d_19)



.webp?sfvrsn=f2a2c343_9)

