What is a Colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy enables visual inspection by a medical examiner of the entire large bowel (also called the colon or large intestine). The procedure is a safe and effective means of evaluating the large bowel. A very clear image of the inside of the bowels can be visualised through a video camera attached to the end of the scope. The camera connects to a computer, which can store and print colour images selected during the procedure.
Why is Colonoscopy done?
Colonoscopy may be done for a variety of reasons. The vast majority of colonoscopies are performed as part of screening programs to diagnose colon cancer.
Value-Based Health Care Benefits
Patients
- Lower costs
- Better outcome
Providers
- Higher patient satisfaction rates
- Better care efficiencies
Payors
- Stronger cost controls
- Reduced risks
Society
- Reduced healthcare expenses
- Better overall health
What are Value Driven Outcomes?
Value Driven Outcomes is a simple concept of improving care for patients with an aim to drive down costs. With its fundamental factors based on overall patient wellness and preventive measures, reaching this goal is based on a set of adjustments in how patients receive medical treatment. Overall wellness, quality of care, and preventive screenings all are taken into consideration, ultimately resulting in better healthcare outcomes.
In Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur, we are aiming to make healthcare proactive rather than reactive, preventing problems from occurring before they start. In view of that, we had designed a Value Driven Outcomes (VDO) framework for colorectal cancer, in which pre-set quality indicators were used to determine cost rationalization.
Colonoscopy Quality Indicators (benchmarks)
- Adequate bowel preparation (Boston Bowel Prep Score > score 6 = Good Bowel Prep)
- A poor bowel prep cleanliness caused limited visibility of colon during examination which correlates to the Polyp & Adenoma Detection Rate.
- Caecal intubation rate = ≥ 90%
- The rate of doctor fully inserted the colonoscope into colon to detect any precancerous polyps or lesions.
- Withdrawal Time = ≥ 6 min
- The total amount of time spent during a colonoscopy. A 6-minute withdrawal time is currently the standard of care.
- Polyp Detection Rate (PDR)
- The rate of detecting any precancerous polyp in colon.
- Adenoma Detection Rate (ADR)
- The rate of detecting Adenomas which are generally benign or noncancerous tumour but carry the potential to become adenocarcinomas which are malignant or cancerous.
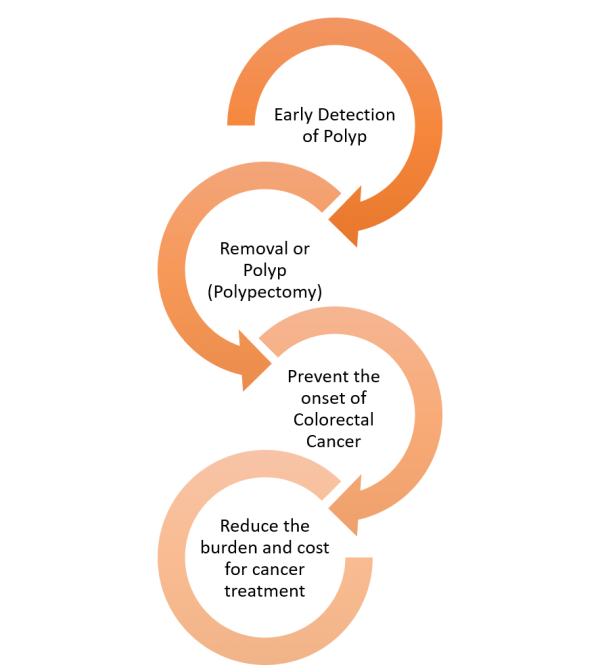
Where does Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur stand
Against Own Hospital Data – Pantai Hospital Kuala Lumpur
| Quality Indicators | Benchmark | 2019 (Oct-Dec) | 2020 (Jan-Dec) | 2021 (Jan-Jun) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Cases | – | 450 | 1414 | 493 |
| Boston Bowel Prep Score (BBPS) (>6 total score) | 95% | 89% | 95% | 96% |
| Caecum Intubation Rate (CIR) | 95% | 95% | 98% | 98% |
| Mean Withdrawal Time (min) | >6-10 min | 8 min | 10 min | 9 min |
| Poly Detection Rate (≥50yo) | 40% | 50% | 55% | 53% |
| Adenoma Detection Rate (≥50yo) | 25% | 23% | 29% | 26% |
| Adenocarcinoma Rate with HPE Report | – | 0.4% | 2% | 1% |
Against International Benchmark
| Clinical Indicators | International Benchmark | 2022 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bowel Prep BBPS (>6 total score) | 95% | 96% | 97% |
| Caecum Intubation Rate (CIR) | 95% | 98% | 100% |
| Mean Withdrawal Time (min) | >6-10 min | 9 min | 11 min |
| Poly Detection Rate (≥50yo) | 40% | 53% | 63% |
| Adenoma Detection Rate (≥50yo) | 25% | 26% | 38% |




.webp?sfvrsn=20763f7d_19)



.webp?sfvrsn=f2a2c343_9)

